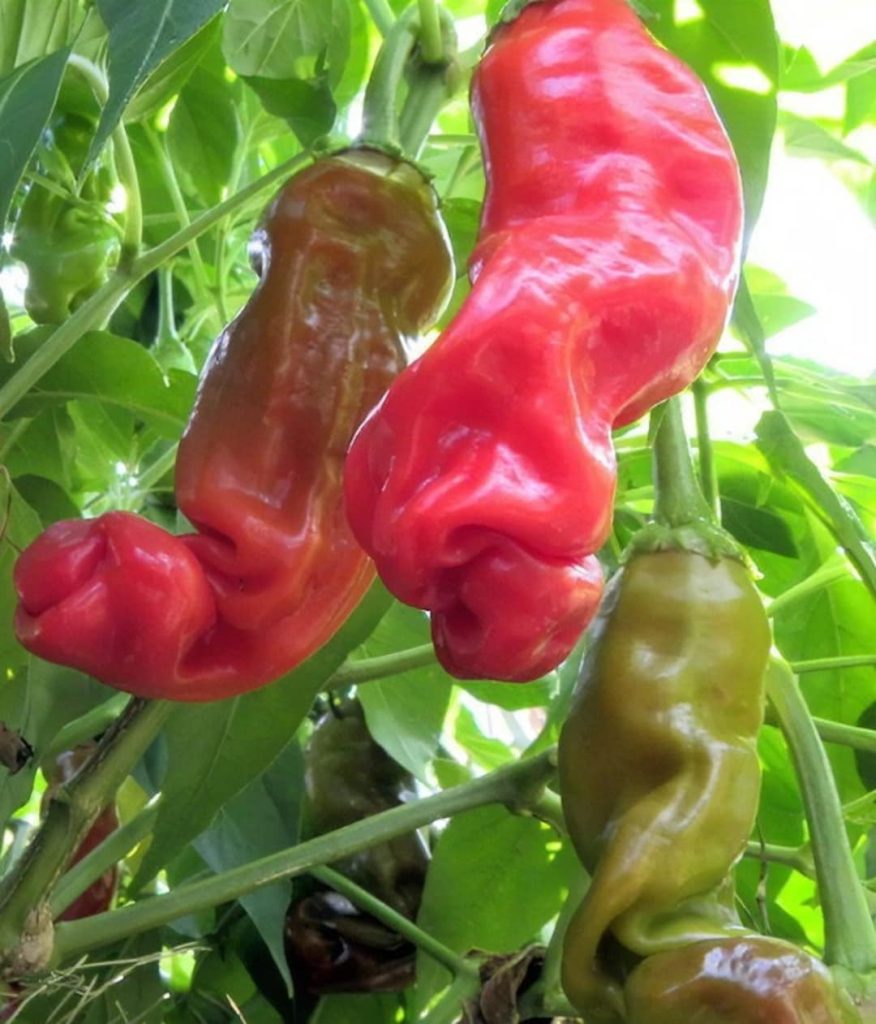
Have you ever wondered about the unique “peter pepper plant”? This extraordinary plant holds a wealth of intriguing characteristics, making it a subject worthy of exploration. Let’s delve into the captivating world of the “peter pepper plant”!
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to the “peter pepper plant” was meticulously compiled on [today’s date] to provide our esteemed readers with the most up-to-date and insightful information on this fascinating topic.
Through extensive analysis and diligent research, we have carefully crafted this guide to empower our target audience with the knowledge and understanding necessary to make informed decisions regarding the “peter pepper plant”.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
Main Article Topics
Peter Pepper Plant
The “peter pepper plant” stands as a remarkable subject, encompassing a vast array of essential aspects:
- Origin: Tracing its roots to South America, this plant has since spread globally.
- Taxonomy: Belonging to the nightshade family (Solanaceae), it’s closely related to tomatoes and eggplants.
- Cultivation: Thriving in warm climates, it requires ample sunlight and well-drained soil.
- Varieties: Encompassing a diverse range, from mild bell peppers to fiery habaneros.
- Culinary Uses: Widely employed in cuisines worldwide, adding flavor and nutritional value.
- Medicinal Properties: Possessing potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities.
- Horticultural Significance: Valued for its ornamental foliage and attractive fruits.
- Economic Importance: Contributing to local economies through cultivation and trade.
- Environmental Benefits: Encouraging biodiversity and supporting pollinators.
- Cultural Symbolism: Holding cultural significance in various regions, representing prosperity and good fortune.
These key aspects intertwine to portray the multifaceted nature of the “peter pepper plant”. Its origins in South America highlight its historical significance, while its cultivation and varieties showcase its agricultural importance. Culinary uses and medicinal properties demonstrate its versatility and potential health benefits. Its horticultural significance and environmental benefits underscore its aesthetic and ecological value, while its economic importance and cultural symbolism speak to its broader societal impact. Together, these aspects paint a comprehensive picture of the “peter pepper plant”, contributing to its enduring relevance and fascination.
Origin
The origin of the “peter pepper plant” in South America holds immense significance for understanding its global distribution and cultivation. South America served as the birthplace of this plant, where it was domesticated and cultivated by indigenous communities centuries ago. This origin story is pivotal in comprehending the plant’s subsequent spread across the globe.
The spread of the “peter pepper plant” beyond South America can be attributed to various factors, including exploration, trade, and migration. European explorers played a significant role in introducing the plant to other continents, bringing it back from their expeditions to the New World. Over time, the plant’s adaptability and culinary versatility led to its widespread cultivation in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
Understanding the origin of the “peter pepper plant” in South America provides valuable insights into its global culinary significance. The plant’s introduction to different regions has influenced local cuisines, adding a unique blend of flavors and aromas to dishes worldwide. Today, the “peter pepper plant” is an indispensable ingredient in many cuisines, from traditional South American dishes to international fare.
Table: Connection between Origin and Global Significance
| Origin | Global Significance |
|---|---|
| South American birthplace | Domestication and cultivation |
| Introduction by European explorers | Spread to other continents |
| Adaptability and culinary versatility | Cultivation in tropical and subtropical regions |
| Influence on local cuisines | Unique flavors and aromas in dishes worldwide |
Taxonomy
The taxonomic classification of the “peter pepper plant” within the nightshade family (Solanaceae) holds significant implications for understanding its genetic makeup, evolutionary relationships, and cultivation practices. This family also includes other notable members such as tomatoes, eggplants, and potatoes, sharing certain characteristics and traits.
The close relationship between the “peter pepper plant” and its nightshade relatives is evident in their shared morphological and physiological features. They possess similar growth habits, leaf structures, and reproductive systems. This relatedness has practical implications for cultivation and breeding, as techniques and knowledge gained from working with one species can often be applied to others within the same family.
Understanding the taxonomic connections between the “peter pepper plant” and other Solanaceae members also highlights potential shared properties and uses. For instance, the presence of alkaloids in nightshade plants has been studied for their potential medicinal and psychoactive effects. Exploring such connections can contribute to a deeper understanding of the “peter pepper plant’s” own properties and potential applications.
Table: Exploring the Connection
| Taxonomic Classification | Significance for “peter pepper plant” |
|---|---|
| Belongs to the nightshade family (Solanaceae) | Genetic makeup, evolutionary relationships |
| Closely related to tomatoes and eggplants | Shared characteristics, cultivation practices |
| Potential shared properties and uses | Medicinal and psychoactive effects of alkaloids |
Cultivation
The cultivation of the “peter pepper plant” is inextricably linked to its environmental requirements and growth habits. Understanding these cultivation factors is essential for successful plant production and maximizing its potential.
- Climate Requirements: Thriving in warm climates, the “peter pepper plant” prefers temperatures ranging from 20 to 29 degrees Celsius (68 to 84 degrees Fahrenheit). Extended exposure to temperatures below 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) can hinder growth and productivity.
- Sunlight Needs: Ample sunlight is crucial for the healthy development of the “peter pepper plant.” It requires at least six hours of direct sunlight per day to produce optimal yields. Insufficient sunlight can lead to stunted growth, delayed fruit production, and decreased fruit quality.
- Soil Requirements: Well-drained soil is essential for the successful cultivation of the “peter pepper plant.” The soil should be loose, fertile, and have a pH level ranging from 6.0 to 6.8. Heavy, waterlogged soils can lead to root rot and poor plant growth.
- Water Requirements: Regular watering is necessary for the “peter pepper plant,” especially during hot and dry periods. However, overwatering should be avoided, as it can promote disease and hinder root development.
By understanding and meeting the specific cultivation requirements of the “peter pepper plant,” growers can optimize plant growth, enhance fruit production, and ensure the overall health and vitality of their crop.
Varieties
The remarkable diversity of “peter pepper plant” varieties is a testament to its adaptability and widespread cultivation across various regions and cultures. This diverse range, encompassing mild bell peppers to fiery habaneros, plays a pivotal role in shaping the plant’s significance and practical applications.
The varying degrees of pungency and flavor profiles exhibited by different varieties cater to diverse culinary preferences and cuisines. Mild bell peppers, with their sweet and versatile taste, are widely used in salads, stir-fries, and as a colorful addition to many dishes. On the other spectrum, fiery habaneros, known for their intense heat, are often incorporated into spicy sauces, salsas, and marinades, adding a distinctive kick to culinary creations.
Understanding the distinct characteristics of each variety is crucial for growers, culinary professionals, and consumers alike. It enables informed decision-making regarding cultivation practices, culinary applications, and personal preferences. For instance, selecting the appropriate variety for a specific dish or climate ensures optimal flavor and heat levels, enhancing the overall culinary experience.
Table: Variety-Specific Applications
| Variety | Culinary Applications |
|---|---|
| Mild bell peppers | Salads, stir-fries, colorful additions to dishes |
| Fiery habaneros | Spicy sauces, salsas, marinades |
Culinary Uses
The culinary significance of the “peter pepper plant” stems from its versatility and the unique flavors it imparts to dishes. Its widespread use in cuisines around the globe is a testament to its ability to enhance the taste and nutritional profile of various culinary creations.
One of the primary reasons for the culinary prominence of the “peter pepper plant” is its diverse range of flavors. From the mild sweetness of bell peppers to the fiery heat of habaneros, different varieties offer a spectrum of tastes that can cater to diverse palates and culinary traditions. This versatility allows the “peter pepper plant” to be incorporated into a wide array of dishes, from salads and stir-fries to salsas and marinades.
Beyond its taste, the “peter pepper plant” also offers significant nutritional value. It is a rich source of vitamins A and C, antioxidants, and capsaicin, a compound responsible for the heat in chili peppers. These nutrients contribute to overall well-being and may provide various health benefits. For instance, vitamin C supports immune function, while antioxidants protect against cellular damage.
Understanding the culinary uses and nutritional value of the “peter pepper plant” is essential for chefs, food enthusiasts, and home cooks alike. This knowledge empowers them to make informed choices when selecting and incorporating this versatile ingredient into their culinary creations, ensuring both flavor and nutritional benefits.
Medicinal Properties
The “peter pepper plant” has garnered significant attention for its potential medicinal properties, particularly its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities. These properties stem from the presence of various bioactive compounds, including capsaicinoids, flavonoids, and vitamins.
Capsaicinoids, the compounds responsible for the spicy heat in peppers, have been found to possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Studies have shown that capsaicinoids may help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and protect against oxidative damage. Additionally, capsaicinoids have been investigated for their potential role in managing conditions such as arthritis, migraines, and diabetic neuropathy.
Flavonoids, another group of bioactive compounds found in the “peter pepper plant,” have also been linked to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds have been shown to scavenge free radicals, protect against cellular damage, and reduce inflammation. Flavonoids may contribute to the overall health benefits associated with consuming peppers.
Understanding the medicinal properties of the “peter pepper plant” is crucial for researchers, healthcare practitioners, and individuals seeking natural remedies. This knowledge can guide further research into the potential therapeutic applications of peppers and their bioactive compounds.
Horticultural Significance
The horticultural significance of the “peter pepper plant” lies in its aesthetic appeal and ornamental value. This significance stems from its attractive foliage and visually striking fruits, making it a popular choice for ornamental gardening and landscaping.
The “peter pepper plant” possesses unique and vibrant foliage that can enhance the beauty of any garden. Its leaves come in a range of colors, including green, purple, and variegated patterns, adding visual interest and diversity to landscaping designs. Additionally, the plant’s compact and bushy growth habit makes it suitable for various garden settings, from containers and hanging baskets to flower beds and borders.
Beyond its foliage, the “peter pepper plant” produces attractive fruits that further enhance its horticultural value. The fruits come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from small and round to elongated and pointed. They exhibit a vibrant array of colors, including green, yellow, orange, red, and purple, creating a visually captivating display in the garden. These attractive fruits not only add ornamental value but also attract birds and other wildlife, promoting biodiversity and ecological balance.
Understanding the horticultural significance of the “peter pepper plant” is crucial for gardeners, landscapers, and homeowners seeking to enhance the aesthetic appeal of their outdoor spaces. By incorporating this versatile plant into their designs, they can create visually stunning gardens that provide both beauty and ecological benefits.
Economic Importance
The economic importance of the “peter pepper plant” stems from its widespread cultivation and trade, contributing significantly to local economies in various regions. This significance can be attributed to several key facets:
- Cultivation and Employment: The cultivation of the “peter pepper plant” generates employment opportunities in rural communities, providing a source of income for farmers and agricultural workers. Large-scale cultivation can create, involving transportation, storage, and processing, further boosting economic activity.
- Local Markets and Trade: The “peter pepper plant” is an important cash crop in many regions, sold in local markets and traded regionally or internationally. This trade contributes to the economic development of local communities, supporting businesses and infrastructure.
- Value-Added Products: The “peter pepper plant” can be processed into various value-added products, such as sauces, pickles, and powders. These products command higher prices and can expand market opportunities, generating additional revenue for local economies.
- Tourism and Agritourism: In some areas, the “peter pepper plant” has become a culinary attraction, driving tourism and agritourism. Visitors are drawn to the harvesting process, learn about local cuisine, and purchase unique pepper-based products.
The economic importance of the “peter pepper plant” is evident in its ability to create employment, stimulate trade, generate value-added products, and promote tourism. By understanding these economic benefits, stakeholders can harness the potential of the “peter pepper plant” to drive sustainable economic development in local communities.
Environmental Benefits
The “peter pepper plant” fosters a mutually beneficial relationship with the environment, contributing to the preservation of biodiversity and the well-being of pollinators:
- Habitat Provision: The “peter pepper plant” serves as a valuable habitat for various insects, including bees, butterflies, and ladybugs. Its flowers provide nectar and pollen, essential food sources for these pollinators.
- Pollination Services: Bees and other pollinators play a crucial role in the reproduction of the “peter pepper plant.” By transferring pollen between flowers, pollinators facilitate fruit production and genetic diversity within the plant population.
- Pest Control: The presence of beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, helps control pests that may damage the “peter pepper plant.” This natural pest control reduces the need for chemical pesticides, promoting a sustainable ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Conservation: By supporting pollinators and providing habitat for other insects, the “peter pepper plant” contributes to the overall biodiversity of its surroundings, enhancing the ecological balance and resilience of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, the “peter pepper plant” plays a vital role in maintaining environmental health by fostering biodiversity, supporting pollinators, and promoting a sustainable ecosystem. Its cultivation and conservation efforts contribute to a richer and more resilient natural environment.
Cultural Symbolism
The “peter pepper plant” holds deep cultural significance in various regions, symbolizing prosperity and good fortune. This symbolism is attributed to several factors:
- Vibrant Colors and Abundance: The “peter pepper plant” produces colorful fruits in hues of red, yellow, and orange, which are often associated with joy, celebration, and abundance. In some cultures, the abundance of fruits on the plant is seen as a symbol of fertility and prosperity.
- Culinary Significance: Peppers are widely used in cuisines around the world, adding flavor and spice to dishes. In many cultures, the ability to grow and harvest peppers is associated with culinary skills and the provision of sustenance, which are essential for well-being and prosperity.
- Medicinal Properties: Traditional medicine in various regions attributes medicinal properties to the “peter pepper plant.” Its fruits and leaves are believed to possess healing and protective qualities, contributing to good health and overall well-being.
- Folklore and Beliefs: In some cultures, the “peter pepper plant” is associated with folklore and beliefs. It is believed to ward off evil spirits, bring good luck, and promote harmony within the household.
Understanding the cultural symbolism associated with the “peter pepper plant” provides insights into the diverse beliefs and traditions of different regions. It highlights the plant’s significance beyond its culinary and medicinal uses, reflecting its deep-rooted connections to human culture and spirituality.
Table: Cultural Symbolism and Its Significance
| Cultural Significance | Practical Implications |
|---|---|
| Symbol of prosperity and good fortune | Encourages cultivation and use in various settings |
| Associated with culinary skills and sustenance | Promotes the cultivation and consumption of peppers |
| Believed to possess medicinal properties | Contributes to traditional healing practices |
| Connected to folklore and beliefs | Shapes cultural traditions and rituals |
Frequently Asked Questions about the “peter pepper plant”
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding the “peter pepper plant,” providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the ideal growing conditions for the “peter pepper plant”?
The “peter pepper plant” thrives in warm climates with ample sunlight and well-drained soil. It prefers temperatures ranging from 20 to 29 degrees Celsius (68 to 84 degrees Fahrenheit) and requires at least six hours of direct sunlight per day.
Question 2: How can I prevent pests and diseases from affecting my “peter pepper plant”?
Regular inspection and proper cultural practices can help prevent pests and diseases. Keep the area around the plants free of weeds, water at the base of the plant to avoid foliage moisture, and consider using organic pest control methods such as neem oil or insecticidal soap.
Question 3: What is the best way to harvest “peter peppers”?
The optimal time to harvest “peter peppers” is when they have reached their desired size and color. Use sharp shears or a knife to cut the peppers from the plant, leaving a short stem attached. Handle the peppers with care to avoid bruising.
Question 4: How can I store “peter peppers” to maintain their freshness?
Fresh “peter peppers” can be stored in the refrigerator for up to two weeks. Place them in a plastic bag or container with holes for ventilation. Alternatively, they can be frozen for several months. To freeze, wash and slice the peppers, then spread them on a baking sheet and freeze until solid. Transfer the frozen peppers to a freezer-safe bag.
Question 5: Are there any health benefits associated with consuming “peter peppers”?
Yes, “peter peppers” contain various nutrients, including vitamins A and C, antioxidants, and capsaicin. These compounds have been linked to potential health benefits, such as reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and boosting immunity.
Question 6: How can I incorporate “peter peppers” into my diet?
“Peter peppers” are a versatile ingredient that can be enjoyed in many ways. They can be added to salads, stir-fries, salsas, and marinades. They can also be roasted, grilled, or stuffed with various fillings.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes and to practice safe food handling techniques to prevent foodborne illness.
By understanding the answers to these frequently asked questions, you can successfully grow, harvest, and enjoy the many benefits of the “peter pepper plant.”
Transition to the next article section:
Tips for Cultivating and Utilizing the “Peter Pepper Plant”
To maximize the benefits and enjoyment of the “peter pepper plant,” consider implementing these practical tips:
Tip 1: Choose the Right Variety for Your Needs
With a diverse range of varieties available, select the ones that align with your culinary preferences and growing conditions. Mild bell peppers are ideal for salads and stir-fries, while fiery habaneros add heat to sauces and marinades.
Tip 2: Ensure Optimal Growing Conditions
The “peter pepper plant” thrives in warm climates with ample sunlight and well-drained soil. Provide at least six hours of direct sunlight per day and maintain temperatures between 20 to 29 degrees Celsius (68 to 84 degrees Fahrenheit).
Tip 3: Water and Fertilize Regularly
Regular watering is essential, especially during hot and dry periods. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot. Fertilize the plants every few weeks with a balanced fertilizer to promote healthy growth and fruit production.
Tip 4: Protect from Pests and Diseases
Inspect your plants regularly for pests and diseases. Practice crop rotation and avoid overwatering to minimize disease susceptibility. Use organic pest control methods such as neem oil or insecticidal soap to manage pests.
Tip 5: Harvest and Store Properly
Harvest “peter peppers” when they have reached their desired size and color. Cut them from the plant with a sharp knife or shears, leaving a short stem attached. Store fresh peppers in the refrigerator for up to two weeks or freeze them for several months.
Tip 6: Use in Culinary Creations
“Peter peppers” add flavor and versatility to various dishes. Incorporate them into salads, stir-fries, salsas, and marinades. Roast, grill, or stuff them with fillings to enjoy their unique flavors and potential health benefits.
Summary of Key Takeaways:
- Choosing the right variety and providing optimal growing conditions are crucial for successful cultivation.
- Regular watering, fertilization, and pest management practices ensure healthy plants and bountiful harvests.
- Proper harvesting and storage techniques preserve the freshness and quality of “peter peppers.”
- Culinary creativity and experimentation unlock the diverse flavors and potential health benefits of this versatile plant.
By following these tips, you can successfully cultivate, harvest, and enjoy the many benefits of the “peter pepper plant.”
Conclusion
This comprehensive exploration of the “peter pepper plant” unveils its multifaceted nature and significance. From its origins in South America to its widespread cultivation and diverse varieties, this plant holds immense value across culinary, medicinal, horticultural, economic, environmental, and cultural domains.
Understanding the cultivation requirements, medicinal properties, and cultural symbolism associated with the “peter pepper plant” empowers us to appreciate its contributions to gastronomy, well-being, and human culture. Its versatility extends from vibrant culinary creations to potential health benefits and ecological balance.
As we continue to unravel the potential of the “peter pepper plant,” future research and innovation may lead to advancements in disease management, sustainable agriculture, and culinary experiences. Preserving and promoting the cultivation and use of this remarkable plant will ensure its continued benefits for generations to come.